At Zaic Design LLC, we understand that automation is the future of the manufacturing industry. We are committed to providing our clients with the custom automation solutions that best meet their specific needs. Our team of engineers and designers have the expertise and experience to tackle the most daunting challenges. We’re always improving, working to better our customized solutions and make your project a success!
A Brief Intro to Automation in Manufacturing
“ Innovation is the outcome of a habit, not a random act. ”
Sukant Ratnakar
Automation is a broad term and can refer to various technologies, including robots, computer-controlled machines, and automated production lines. Even though it has been around for centuries, automation has only recently become essential in many factories and other industrial settings. Industrial automation has revolutionized manufacturing by increasing productivity, reducing costs, and improving product quality.
The History of Automation in Manufacturing
What Was the First Industrial Automata?
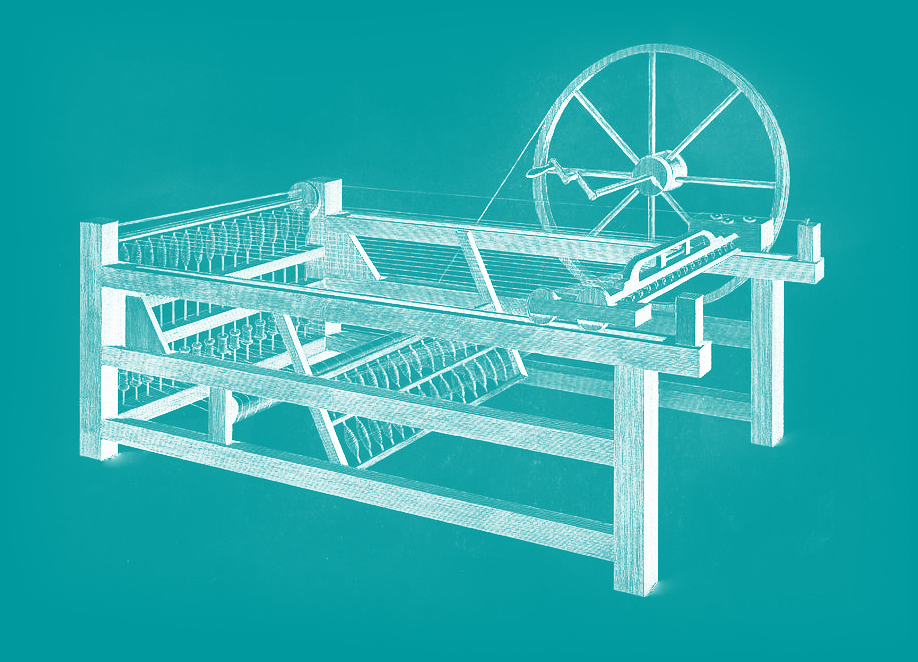
The first automated machine was known as the Spinning Jenny. Invented by James Hargreaves in 1764, the machine could simultaneously spin multiple threads, dramatically increasing the productivity of the textile industry. This machine was the first in what would become a series of increasingly complex and useful automations, that have shaped our modern way of life.
Automation During the 1900s
The first half of the 20th century was a period of rapid growth for the automation industry. The Industrial Revolution had enabled a broader capacity for goods production and factories were increasingly using automated machines to meet burgeoning demand. However, these early machines were often unreliable and required constant maintenance and attention.
In the 1950s, Japanese engineer Taiichi Ohno developed the Toyota Production System, which incorporated automation to greatly improve efficiency and quality. His system focused on reducing waste and inspired many modern concepts like “Just-In-Time” inventory and Kaizen (continuous improvement) philosophy. Seeing this new system’s potential, other Japanese manufacturers adopted it and used it to speed-up production, eventually becoming leaders in the global automotive market.
In the 1980s, automation became increasingly critical to the food and beverage industry. Much of this uptick was due to further technological advances, which made automation more affordable and reliable.
The 1990s saw the steady adoption of lean manufacturing, a production approach that emphasizes peak efficiency. Lean manufacturing relies heavily on automation to achieve its goals of reducing waste, shortening lead-times, and cutting down on the storage of physical inventory.
Did you know?
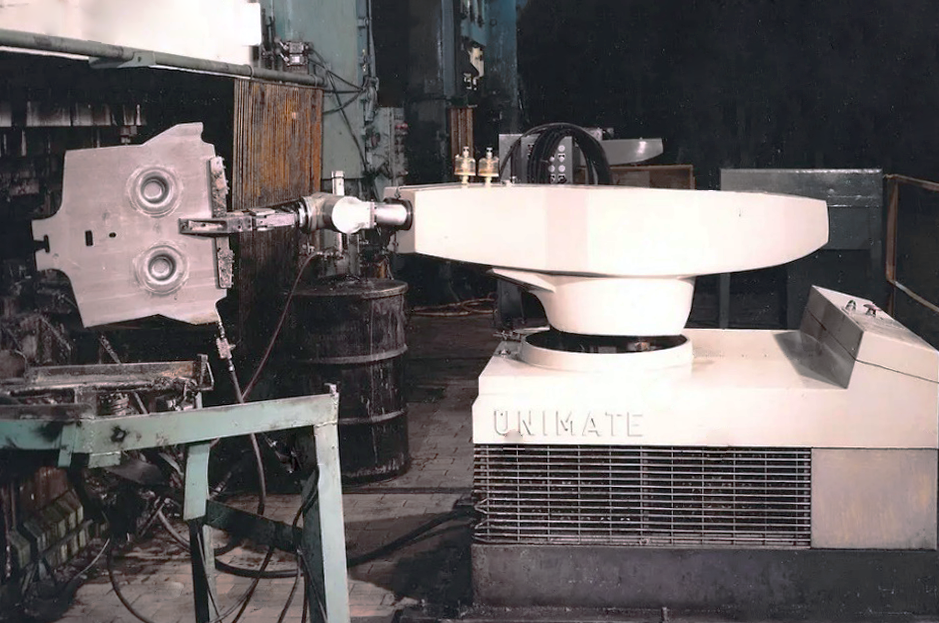
In 1961, the first industrial robot was installed on the assembly line of a General Motors car factory in Ewing, New Jersey, only a few miles from our headquarters in Princeton.
The robot, called UNIMATE, was designed by Joseph Engelberger and George Devol. UNIMATE was capable of welding heavy parts together and utilized sensors that would prevent it from colliding with other objects or people.
Automation Today
The 21st century has been a time of continued innovation in the automation industry. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning have made it possible for machines to become increasingly intelligent and adaptive. Additionally, this century has shown us the rise of Industry 4.0, or a 4th Industrial Revolution, that champions interconnectivity and seamless communication between software, hardware, data, and manufacturing. Another exciting development is the growth of smart factories, which are highly automated, adaptable, and connected to the internet of things.
One of the most influential changes has been the integration of Robot technology. Robots can now communicate with, smart devices, machinery, and even each other, making them more effective and efficient, in factory settings. They can also adapt to changing conditions and learn from their mistakes. All this makes them well-suited for tasks that are hazardous, difficult, or unpleasant for people, such as working with dangerous machinery or dealing with toxic materials.
Cobots (collaborative robots) are also becoming increasingly affordable and available, making them more accessible to businesses of all sizes. As automation continues to march forward, Cobots will likely become great advantages to the companies that employ them.
The Present State of Automated Manufacturing
And Why Industry Experts Are Always Working to Improve It
The Benefits of Automation
Every day, companies are successfully implementing automation into their production schedules. Some of the advantages they have discovered are:
- Machine learning unlocks adaptability – Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on developing computer programs that can learn from data. This means that they can improve their own performance as they receive more information. Machine learning is being used extensively in automation to create systems that can better adjust to dynamic environments. One of the most notable examples is the invention of self-driving cars. Autonomous vehicles rely on machine learning algorithms and high-tech sensors to perceive their surroundings and make decisions accordingly. With this technology, automakers can create cars that are capable of driving themselves in a wide variety of conditions.
- Interconnected equipment saves time – Some production equipment, commonly used in factories, include robots, assembly lines, and 3D printers. Once interconnected, production equipment can be leveraged to help factories create products more efficiently, by cutting down on repeat data entry and mistakes. Additionally, assembly lines can help factories produce products faster by setting the pace and systematically moving product through the production process.
- Smart manufacturing software streamlines production – Advanced software can help to streamline the manufacturing process by automating tasks and providing real-time data about the production process. This software is implemented extensively in Industry 4.0, as it helps factories communicate with sales, affording more efficiency and responsiveness to changes in customer demand.
- Cobots are dependable assistants – Cobots work side-by-side with people to help them complete tasks. For instance, a cobot might assist a technician with assembling, testing, and painting products. Cobots are increasingly being relied upon for support with manufacturing, as they can help maintain a high degree of precision and safety, while performing repetitive tasks.
- Automation facilitates safety and reduces waste – Automation can help to improve working conditions by reducing the need for people to preform hazardous tasks, like handling dangerous materials or working in remote environments. Automation also encourages waste reduction by ensuring that products are made to precise specifications. This means there will be less need for rework or scrap, which can save factories money and improve their bottom line.
How Fortune 500 Companies Are Thriving with Automated Manufacturing
As we know, skilled labor is in short supply. Manufacturers who used to operate their facilities with two or three shifts per day are finding it difficult to fill the schedule and keep pace with demand. Many of the most successful companies are beginning to use automation to fill necessary gaps. When automated appropriately, efficiency and speed improve dramatically, allowing companies to flourish in a constantly changing world.
Possible Challenges and Limitations of Automated Systems
As we have seen, automation has many advantages and can be a benefit to almost every industry. However, there are some challenges and obstacles that may stand in the way of easy integration:
- May require a high capital expenditure – One of the main limitations of automation is that it often requires a substantial up-front investment. This can make automation unaffordable for small and medium-sized businesses. However, with the increased productivity afforded by automation, over time, companies will find that their investment has become a net savings.
- Machines tailor-made for a specific function can become obsolete – Automated systems can become out-of-date or redundant when the processes or products they were designed for change. For example, if a company updates its product range, the automation system they use may need to be reworked or replaced entirely. This can be costly and time-consuming to correct. However, we can work with you to identify potential upcoming changes and design with longevity in mind.
- Could introduce different safety risks – While automation can improve safety in many ways, it can also create additional hazards. If operating conditions change unexpectedly, or employees interact with the robots inappropriately, automated systems may not be able to recognize the situation and adapt in time, potentially leading to accidents.
- Some systems need extra maintenance or support – Automated systems are often complex and may require specialist knowledge to maintain and repair them. We design our systems, with your input, and work to create the custom routines that will best integrate with your facility and established practices.
- Possible worker displacement – One of the most controversial aspects of automation is its potential to replace workers and skilled laborers. As automated systems become more advanced, they can perform a wider range of tasks, resulting in people being replaced by machines in many industries. However, in many circumstances, an automated system can fill a role that is difficult to staff due to its hazards, monotony, or physical demands.
- Some amount of human intervention is still required – Even the most advanced automated systems still require some level of engagement and intervention. In contrast to the last point, there are still many tasks that machines are not able to preform as well as people. Despite how useful machines can be in manufacturing, they are still a part of the process and not the whole.
Our Skilled Team can help you overcome the challenges of automation and realize the numerous advantages. We will meet with you to recognize and fully assess your needs.
Once we understand your production goals, we will draft the automated solution, test it through rigorous feasibility studies, and propose how to best integrate it into your existing or planned operations. When we have built the machine, we will install it at your facility, write user manuals, provide technical certifications and offer training for your staff. Even long after our machine has become a reliable part of your manufacturing process, we can assist with maintenance or later modifications.
Businesses of any size could benefit from automation. Businesses all around the world are already integrating automation and seeing impressive results! Don’t let your business fall behind – automation is the future and we are here to help make that future your reality.



0 Comments